Table of Contents
Every mobile app runs on a foundation of technology choices. From the buttons users tap to the database that stores their information, every layer depends on a specific mix of tools, frameworks, and programming languages. This combination is what we call a tech stack.
For businesses, choosing the right tech stack is just as important as defining app features. A poor choice may lead to performance issues, lack of scalability, or even security risks. On the other hand, the right stack brings speed, stability, and adaptability.
Since each industry has unique requirements—like compliance in healthcare, high-security needs in finance, or real-time data in oil and gas—the stacks used can differ significantly.
This blog takes a detailed look at popular mobile app tech stacks, their components, and where they fit best across industries.
What is a Tech Stack in Mobile Apps?
A tech stack is the set of technologies used to build and run a mobile application. It combines programming languages, frameworks, libraries, tools, and databases to create both the frontend (what users see) and the backend (the engine behind the scenes).
Think of a mobile app like a restaurant:
- The frontend is the dining area—the menus, seating, and overall experience.
- The backend is the kitchen—where orders are processed, food is cooked, and everything comes together.
- The database is the storage room, holding all the ingredients (data) needed to keep things running.
In mobile apps, the tech stack determines:
- User experience: How smooth and fast the app feels.
- Performance: Whether it can handle 100 or 1 million users.
- Security: Protecting user data and transactions.
- Scalability: Supporting growth without crashing.
- Maintenance: How easy it is to update and add new features.
Because of these factors, businesses in different industries often rely on different tech stacks.
Core Components of a Mobile App Tech Stack
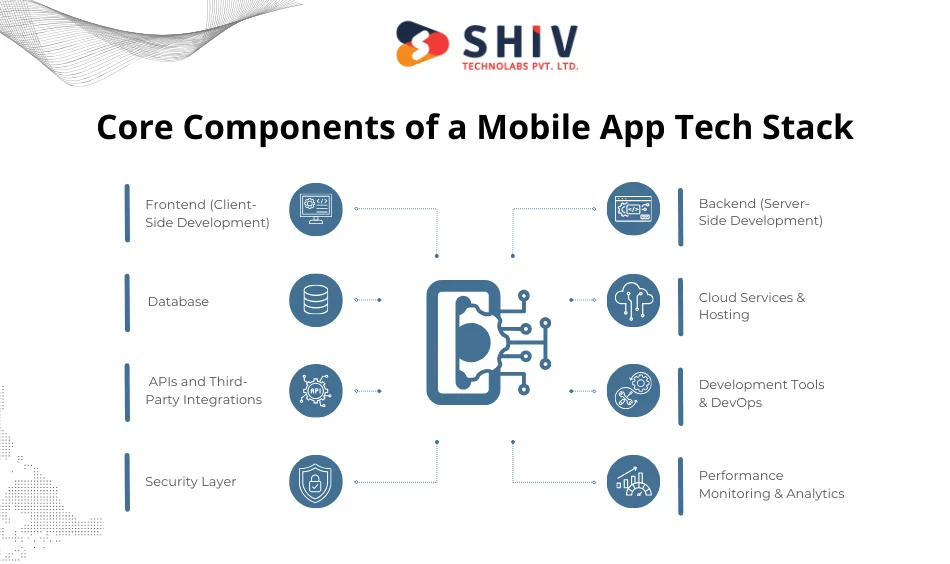
Every mobile app tech stack is made up of multiple layers. Let’s break down the key components:
1. Frontend (Client-Side Development)
The frontend is what users interact with directly. It includes the app’s interface, design, and overall usability. For mobile apps, developers can build frontends in two ways:
Native Development
- Uses platform-specific languages.
- For iOS: Swift or Objective-C.
- For Android: Java or Kotlin.
- Pros: Best performance, smooth user experience, full access to device hardware.
- Cons: Requires building two separate apps for iOS and Android.
- Uses frameworks that let one codebase run on both iOS and Android.
- Popular tools: React Native, Flutter, Xamarin.
- Pros: Faster development, lower cost, single codebase.
- Cons: Sometimes less optimized compared to native apps.
2. Backend (Server-Side Development)
The backend is the engine that powers the app. It manages business logic, user authentication, transactions, and communication with the database.
Programming Languages & Frameworks:
- Node.js (JavaScript runtime for real-time apps).
- Django (Python-based, secure, fast).
- Spring Boot (Java-based, robust).
- Ruby on Rails (Ruby-based, efficient for startups).
Key Functions of Backend:
- Data processing.
- Authentication & authorization.
- Integration with APIs (payments, maps, social logins).
- Managing requests between the app and server.
3. Database
Databases store and manage app data, such as user profiles, product catalogs, or medical records.
Relational Databases (SQL)
- Examples: MySQL, PostgreSQL.
- Best for structured data, financial apps, e-commerce.
# Non-Relational Databases (NoSQL)
- Examples: MongoDB, Firebase Realtime Database.
- Best for unstructured data, chat apps, media-heavy apps.
4. Cloud Services & Hosting
Modern mobile apps rely heavily on cloud infrastructure for scalability and performance.
Popular Providers:
- AWS (Amazon Web Services).
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Microsoft Azure.
Benefits:
- On-demand scalability.
- Global availability.
- Built-in tools for security, storage, and analytics.
5. APIs and Third-Party Integrations
Most apps need external services to enhance functionality. Instead of building everything from scratch, developers connect APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
Common APIs:
- Payment gateways (Stripe, PayPal).
- Messaging & push notifications (Firebase Cloud Messaging, Twilio).
- Maps & location (Google Maps, Mapbox).
- Analytics (Google Analytics, Mixpanel).
APIs reduce development time while ensuring apps have essential modern features.
6. Development Tools & DevOps
To manage coding, testing, and deployment, developers use:
- GitHub / GitLab for version control.
- Jenkins / CircleCI for continuous integration.
- Docker & Kubernetes for containerization and orchestration.
These tools allow teams to collaborate, test, and release apps faster.
7. Security Layer
No tech stack is complete without security. Industries like banking, healthcare, and oil & gas demand high levels of protection.
Security Practices:
- Data encryption (SSL/TLS).
- Two-factor authentication.
- Role-based access controls.
- Compliance standards (HIPAA, GDPR, PCI-DSS).
8. Performance Monitoring & Analytics
Finally, apps need tools to monitor performance and user behavior.
- Crashlytics for error reporting.
- New Relic for performance tracking.
- Firebase Analytics for user insights.
These tools help developers maintain smooth experiences and make data-driven improvements.
Popular Tech Stacks for Mobile Apps
There’s no single best tech stack for all mobile apps. Each comes with strengths that suit specific goals, industries, and business needs. Below, we look at some of the most popular stacks shaping mobile development today.
1. MEAN / MERN Stack
The MEAN and MERN stacks are two of the most common technology bundles for building mobile and web apps.
- MEAN: MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js.
- MERN: MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js.
Both use JavaScript for frontend and backend, which reduces complexity since developers work in one language across the app.
Why It’s Popular:
- End-to-end JavaScript simplifies development.
- MongoDB offers flexibility for handling structured and unstructured data.
- Strong community support with libraries and plugins.
- Easy to scale as the user base grows.
Industries That Rely on MEAN/MERN:
- eCommerce: For apps that need product catalogs, cart management, and quick loading.
- Education: Online learning platforms with interactive features.
- Healthcare: Apps that require scalable data handling (e.g., patient portals).
Pros:
- Single language across full stack → reduced learning curve.
- Good for MVPs and fast launches.
- Open-source tools keep costs down.
Cons:
- Real-time performance is not always the best.
- Angular (MEAN) has a steeper learning curve.
- Heavy apps may face scaling issues compared to native stacks.
2. Flutter + Firebase
Google’s Flutter framework has become one of the fastest-growing tools for cross-platform mobile development. Paired with Firebase (Google’s cloud-based backend-as-a-service), it makes a powerful tech stack for startups and enterprises alike.
- Flutter: A UI toolkit for building natively compiled apps from one codebase.
- Firebase: Provides hosting, real-time database, authentication, analytics, and cloud storage.
Why It’s Popular:
- Developers can build Android and iOS apps from a single codebase.
- Pre-built widgets make UI development faster.
- Firebase handles backend complexities like authentication and cloud storage.
- Strong backing from Google.
Industries That Rely on Flutter + Firebase:
- Startups: Ideal for quick MVPs.
- Healthcare: Patient-doctor communication apps with real-time data.
- Education: Apps with live sessions and chat features.
- Retail: Loyalty apps and customer engagement tools.
Pros:
- Faster development cycles.
- Lower cost since one team can handle both platforms.
- Firebase offers real-time sync, great for messaging and alerts.
Cons:
- App size can be larger compared to native apps.
- Some advanced features may still need native code.
- Firebase pricing may increase with scale.
3. React Native + Node.js

React Native, developed by Meta (Facebook), is one of the most widely used frameworks for cross-platform development. When combined with Node.js as the backend, it creates a stack that excels in real-time, scalable applications.
- React Native: Builds apps for iOS and Android using JavaScript and React principles.
- Node.js: A JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 engine, known for event-driven, non-blocking I/O.
Why It’s Popular:
- Single codebase for iOS and Android.
- Large ecosystem and community support.
- Node.js enables apps with high-speed data and real-time communication.
- Strong developer pool worldwide.
Industries That Rely on React Native + Node.js:
- Logistics & Transportation: Real-time GPS tracking and driver apps.
- Social Apps: Chat, feed, and media-heavy platforms.
- Oil & Gas: Suitable for logistics, social apps, and Oil & Gas field operations.
Pros:
- Wide adoption = availability of skilled developers.
- Performance is close to native.
- Node.js backend supports APIs, IoT, and high-traffic apps.
Cons:
- Complex animations may not perform as well as native.
- Debugging can get tricky in larger projects.
- Dependency on third-party libraries for some features.
4. Kotlin/Java + Spring Boot
Kotlin and Java remain the main languages for Android app development. When paired with Spring Boot as a backend framework, they create a reliable and secure tech stack.
- Kotlin/Java (Frontend): Both are officially supported for Android development. Kotlin is newer, concise, and less error-prone, while Java is mature with massive libraries.
- Spring Boot (Backend): A Java-based framework known for building robust, scalable backend systems.
Why It’s Popular:
- Backed by Google and widely used in enterprise Android development.
- High security and strong performance for apps handling sensitive data.
- Large ecosystem of tools, libraries, and developer talent.
Industries That Use Kotlin/Java + Spring Boot:
- Finance: Banking and payment apps where security is non-negotiable.
- Enterprise: Internal productivity tools and ERP apps.
- Healthcare: Patient record systems need strict compliance.
Pros:
- Mature and stable ecosystem.
- Kotlin reduces boilerplate code, speeding development.
- Spring Boot simplifies backend setup.
Cons:
- A separate codebase is required for iOS.
- Development can take longer compared to cross-platform frameworks.
- Java projects may be more resource-heavy.
5. Swift + Core Data + Vapor
For iOS development, Swift is the go-to language. When paired with Core Data (Apple’s persistence framework) and Vapor (a popular Swift backend framework), it creates a full-stack solution for Apple-focused apps.
- Swift (Frontend): Modern, fast, and safe programming language for iOS.
- Core Data (Database): Manages model layer objects in iOS apps.
- Vapor (Backend): A server-side Swift framework.
Why It’s Popular:
- Offers the best performance and integration with Apple hardware.
- Ensures smooth user experience for iOS apps.
- Strong security features are baked into the ecosystem.
Industries That Use Swift + Core Data + Vapor:
- Retail: High-end shopping apps with rich UI.
- Healthcare: iOS-focused health monitoring apps.
- Media & Entertainment: Streaming apps and interactive platforms.
Pros:
- Best option for iOS performance.
- Strong Apple ecosystem support.
- Core Data simplifies local storage needs.
Cons:
- iOS only, not cross-platform.
- Requires a separate team for Android.
- Smaller backend community compared to Node.js or Django.
6. Unity/Unreal Engine + C#/C++
For gaming and high-performance apps, Unity and Unreal Engine dominate the space. They pair with C# (Unity) or C++ (Unreal Engine) for creating rich, immersive experiences.
- Unity: Popular for 2D and 3D games, AR/VR, and interactive apps.
- Unreal Engine: Known for high-end graphics, AAA games, and advanced visual effects.
Why It’s Popular:
- Offers real-time 3D rendering and physics engines.
- Strong support for AR/VR and next-gen graphics.
- Active communities and marketplace for assets.
Industries That Use Unity/Unreal + C#/C++:
- Gaming: Mobile, console, and PC games.
- Entertainment: VR concerts, interactive media.
- Education: Gamified learning apps and simulations.
Pros:
- Rich graphics and immersive experiences.
- Large community support with plugins and assets.
- Flexible enough for industries beyond gaming.
Cons:
- Performance-heavy, requiring powerful devices.
- Larger file sizes for apps.
- Complex learning curve for beginners.
How to Choose the Right Stack for Your Mobile App?

With so many stacks available, choosing the right one may feel overwhelming. The best way is to evaluate your project based on a few practical factors.
1. Define Your App Goals
Are you building an MVP to test an idea? → Choose faster, cost-effective stacks like Flutter + Firebase.
Need an enterprise-grade solution? → Go for Kotlin/Java + Spring Boot or Swift + Vapor for iOS.
2. Consider Target Platforms
- If you want Android-only apps, Kotlin/Java is best.
- If you want iOS-only apps, Swift is the obvious choice.
- For cross-platform apps, React Native or Flutter offers strong support.
3. Industry Requirements
Different industries demand different features:
- Finance: High security, reliable backend (Kotlin/Java + Spring Boot).
- Healthcare: Data compliance and scalability (Flutter + Firebase or MERN).
- Education: Video, chat, real-time features (MEAN/MERN, Flutter).
- Retail: Smooth UX and payment integration (React Native + Node.js).
- Gaming: Advanced graphics (Unity/Unreal).
4. Scalability & Performance Needs
- High-traffic apps with real-time updates → React Native + Node.js.
- Apps that need smooth animations and rich graphics → Swift or Unity.
5. Development Resources
- If you already have an in-house team skilled in JavaScript, MERN/MEAN, or React Native makes sense.
- If your team specializes in Kotlin or Swift, sticking to native may be faster and safer.
Trends in Mobile App Tech Stacks
Technology is never static. New frameworks and integrations are shaping how mobile apps are built.
1. Rise of Cross-Platform Frameworks
Flutter and React Native continue to dominate as businesses want apps that run on both iOS and Android with one codebase.
2. AI and Machine Learning Integration
- AI-driven personalization, chatbots, and predictive analytics are becoming standard.
- Popular ML tools include TensorFlow Lite (Android), Core ML (iOS), and Firebase ML Kit.
3. 5G and Edge Computing
- Faster speeds enable richer mobile experiences (AR/VR, HD streaming).
- Stacks need to integrate with low-latency cloud solutions.
4. AR/VR Development
- Unity and Unreal are driving immersive apps in education, healthcare, and entertainment.
- ARKit (iOS) and ARCore (Android) expand mobile capabilities further.
5. Cloud-Native Apps
- AWS Amplify, Firebase, and Azure Mobile Apps simplify backend needs.
- Microservices architecture is replacing monolithic systems for better scalability.
6. Security by Design
- With rising data breaches, mobile stacks now integrate stronger encryption and compliance-ready frameworks.
- Healthcare and finance apps especially demand this shift.
Conclusion
There’s no universal answer to “What is the best tech stack for mobile apps?”. The right choice depends on your app’s purpose, industry needs, scalability goals, and team expertise.
- If speed and cost matter most → go cross-platform with Flutter + Firebase or React Native + Node.js.
- If security and compliance are top priority → stick with Kotlin/Java + Spring Boot or Swift + Vapor.
- For graphics-heavy apps → Unity/Unreal Engine is unmatched.
A smart approach is to start with your goals, match them with the stack’s strengths, and think long-term—because once your app is live, changing stacks can be costly.
👉 If you’re planning to build a mobile app and want expert guidance on picking the right stack, you can connect with our mobile app development services team at Shiv Technolabs.
With years of experience across industries, Shiv Technolabs helps businesses select stacks that not only support current needs but also prepare them for future growth.
FAQs
Q1. What is a tech stack in mobile app development?
A tech stack is the combination of programming languages, frameworks, tools, and databases used to build and run a mobile app. It includes both frontend and backend components.
Q2. Which tech stack is best for cross-platform mobile apps?
Popular choices include React Native + Node.js and Flutter + Firebase. Both allow building apps for iOS and Android with a single codebase while supporting scalability and modern features.
Q3. Why do industries use different tech stacks for mobile apps?
Each industry has unique needs. For example, finance apps demand security, healthcare apps need compliance, retail apps focus on payments, and gaming apps require advanced graphics.
Q4. Is it better to build native apps or cross-platform apps?
Native apps (Swift, Kotlin/Java) offer the best performance and device integration, while cross-platform apps (Flutter, React Native) save time and cost by running on both iOS and Android.
Q5. What are the most common backend frameworks for mobile apps?
Widely used frameworks include Node.js, Django, Spring Boot, and Ruby on Rails. The choice depends on project requirements such as real-time updates, security, and scalability.
Q6. Which databases are widely used in mobile app development?
SQL databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL are used for structured data, while NoSQL databases like MongoDB and Firebase handle unstructured or real-time data.
Q7. How do I choose the right tech stack for my mobile app?
Consider your app goals, target platforms, scalability needs, industry requirements, and available developer skills before selecting a stack. Cost and long-term maintenance also matter.
Q8. Do you provide mobile app consulting to select the right tech stack?
Yes, expert teams can analyze your requirements, budget, and industry specifics to recommend the most suitable tech stack for your mobile app development project.
Q9. Can I get end-to-end mobile app development services along with tech stack selection?
Absolutely. From planning and design to development and support, full-cycle services are available to help businesses launch mobile apps with the right stack.
Q10. Do you handle maintenance and scaling of apps after launch?
Yes. Ongoing maintenance, feature upgrades, and scaling support ensure that your app stays updated, secure, and ready for growing user demands.

![Popular Tech Stacks Used in Mobile Apps [Industry-wise Bifurcation]](https://shivlab.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Popular-Tech-Stacks-Used-in-Mobile-Apps-Industry-wise-Bifurcation.webp)























