Table of Contents
Banks today manage millions of customers, thousands of enquiries, and vast amounts of financial information daily. However, the division of most institutions takes the form of disjointed systems, archaic tools, and manual processes that drag down teams.
These loopholes directly influence customer satisfaction, compliance, and revenue prospects. Banking software development providers offer services to design CRM-enabled infrastructures that integrate data, customers, and compliance in a single framework to meet the demands of modern banks.
With the rapid growth of digital banking, organizations are moving away from legacy CRM platforms to intelligent ones that can personalize messages, monitor behavior, automate onboarding, facilitate AML/KYC operations, and provide real-time customer intelligence.
The global CRM market is set to grow by over 15% by 2028, underscoring the importance of the quality of the CRM systems used by financial institutions. This article discusses the 10 CRM features that all banks should have in their checklist.
What Is CRM in Banking Software and Why Do Banks Need It?
CRM in Banking Software is the concept of embedding customer relationship management capabilities directly within the core systems of a bank, including customer profiles, loan journeys, communication logs, compliance processes, and financial behavior analytics.
CRM banking software allows combining the experiences of marketing, support, onboarding, and data reporting into a single platform rather than using separate tools. The banks require CRM systems as never before because of:
- Growth in competition posed by digital-only banks.
- High demand for hyper-personalized financial products.
- Tougher regulatory conditions.
- Customers expect quick and smooth customer service.
Conventional stand-alone CRMs can store only simple contact information. But CRM software for financial institutions need not stop there; they should be linked to loan systems, KYC engines, payment records, and compliance modules.
Automated KYC sync, loan processes, analytics, and omnichannel communication.
CRM Types Comparison Table
| CRM Type | Description | Ideal For | Example Functionality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standalone CRM | Basic contact & lead management | Small financial firms | Manual data entry, basic lead tracking |
| Integrated CRM Banking Software | Real-time customer + transaction + loan data | Banks & NBFCs | Automated KYC sync, loan workflows, analytics, omnichannel communication |
What Are the Key Benefits of CRM in Banking Software?
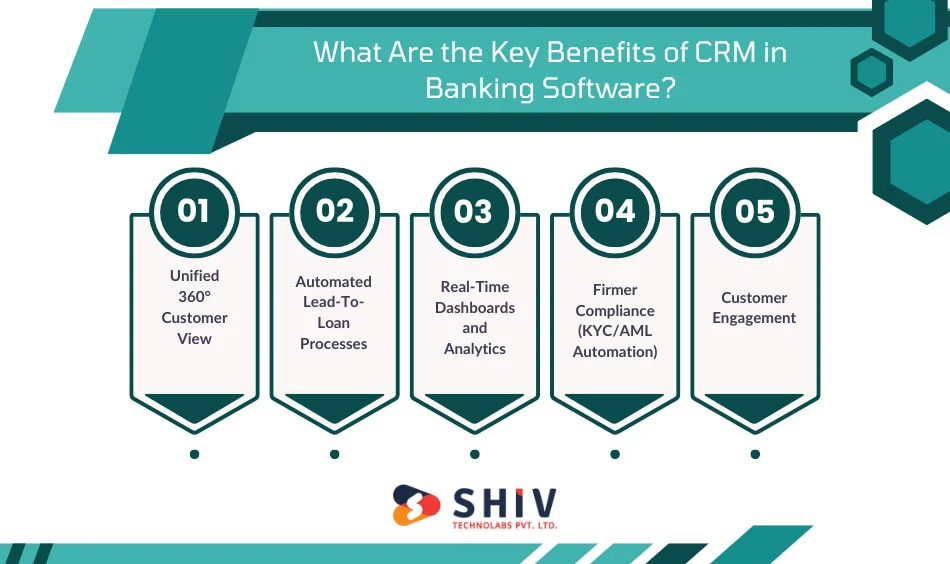
CRM capabilities in banking realize quantifiable benefits in operations, customer experience and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Unified 360° Customer View
Banks receive full insight into deposits, loans, support tickets, payment history, and communication logs, enabling teams to know customers better.
Automated Lead-To-Loan Processes
CRM modules automate scoring, document collection, verification, underwriting and approval and cut the processing time to up to 40%.
Real-Time Dashboards and Analytics
Dashboards track branch performance, loan pipelines, churn risk, and cross-selling opportunities, enhancing decision-making by 30%.
Firmer Compliance (KYC/AML Automation)
Banks can automatically verify identities, monitor red-flag behaviour, and record compliance actions, thereby minimising audit risks.
Customer Engagement
CRM data helps banks provide customized product recommendations, renewal alerts, and proactive calls.
These advantages make banking more competent, responsive, and customer-focused.
What Is the Cost to Implement CRM in Banking Software?
There are numerous variables in the implementation of CRM in Banking Software, including the level of customisation, integration requirements, user count, data migration, and training requirements. Below are the cost factors:
- Customization – personalize workflows, dashboards, automate, and roles.
- API Integrations- KYC engines, payment gateways, core banking, and loan systems.
- Security Improvement – encryption, MFA, access controls.
- Data Migration – importing records of customers.
- User Training- onboarding branch-wide.
Cost Breakdown Table
| Implementation Element | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Basic CRM Module | $15,000 – $25,000 | Suitable for small banks |
| Cloud CRM Integration | $30,000 – $50,000 | Best for mid-size financial institutions |
| Enterprise CRM Platform | $70,000+ | Multi-branch or large banks |
The collaboration with an established banking software development services provider ensures effective planning, secure data structures, and long-term ROI.
Top 10 Features Every Bank Should Include in CRM Banking Software

Contemporary banks are operating in a marketplace environment that has never been as demanding in terms of customer expectations, compliance requirements, and competition. To respond to these demands, banks need to embrace CRM in Banking Software that is not a Customer database but an intelligent engine capable of optimizing operations, enhancing service, and driving financial growth.
The top 10 critical CRM features that banks must have include: personalization, security, more automated workflows, and a cohesive customer experience across branches, digital channels, and support teams.
1. 360° Customer Profile View
All CRM features in the banking industry are based on a complete customer profile. It makes all the interactions, financial products, and transactions available in a single dashboard.
This module includes:
- Current account data and savings data.
- EMI patterns and loan history.
- KYC-documents and status verification.
- Support contacts and previous complaints.
- Behavioral and relationship score knowledge.
CRM in Banking Software will provide employees with an immediate understanding of who the customer is, what they require, and what is best to serve them. This substantially enhances response time and helps create stronger customer relationships.
2. Automated Lead & Opportunity Management
Leads are generated through banks’ websites, branches, mobile applications, campaigns, and third-party channels in the thousands. In manual tracking, opportunities are lost, and follow-ups are not conducted. Key CRM capabilities:
- AI-based lead scoring
- Automated lead assignment
- Loan opportunity tracking
- Relationship managers follow-up alerts.
- Single-view lead pipeline
Bank CRM modules ensure that all leads are captured, nurtured, and converted, thereby enhancing sales and loan disbursal rates.
3. Loan Origination & Approval Workflow
Loan processing is one of the most complex banking business processes. The CRM integration would allow banks to automate and streamline the process.
The generic CRM powered loan workflow:
- Verification and uploading of documents.
- Computerized income and credit verification.
- Underwriting and approval routing.
- Disbursement tracking
- Digital application collection
CRM-enabled lending processes in banks decrease loyalty processing up to 35% and reduce compliance errors.
4. KYC & AML Compliance Monitoring
Manual compliance with the regulations is unscalable. Banking Software CRM should have in-built compliance intelligence. What this feature includes:
- Automated KYC verification
- Monitoring AML patterns of behavior.
- Live watchlist and PEP screening.
- Religion is known as suspicious activity reporting.
- Audit logs for regulators
For banks building digital products around compliance, these controls pair well with specialised fintech development services that cover payments, onboarding, and real-time checks.
This minimizes audit risks and fraud, and facilitates the seamless integration of new customers.
5. AI-Powered Customer Insights
Artificial intelligence converts raw data into something they can do something with- it assists teams to know what customers want before they even ask.
AI analysis covers:
- Customer churn prediction
- Tendency to purchase loans or insurance.
- Trend of deposit and withdrawal.
- Perfect upsell and cross-sell prospects.
- Risk scoring and segmentation.
With a better conversion rate, banks are able to make specific campaigns and customized financial products. Financial institutions that want deeper AI models can also work with AI development services to craft banking-grade models for risk, experience, and fraud.
6. Omnichannel Communication Integration
Be it a branch, mobile application, chatbot, email, or WhatsApp interaction, CRM aspects in the banking sector should ensure that all this is captured in a single timeline.
What omnichannel CRM offers:
- Cohesive communication history.
- Automated message triggers
- Team instant notifications.
- One-to-one campaigns on channels of choice.
- Smooth transition of support teams.
This will prevent the customer from entering the same information and ensure the same type of service is provided.
7. Task Automation & Workflow Management
Banks perform thousands of tasks daily, such as renewals, verifications, follow-ups, reminders, and escalations. Manual labor is time-consuming and can lead to bottlenecks.
CRM automation handles:
- Follow-up scheduling
- EMI reminders
- Policy renewal alerts
- Reminders regarding document submission.
- Manager approval flows
- Ticket escalations
Efficiency, reduced human error, and reduced staff workload are among the benefits of automation in enhancing human expertise in customer engagement.
8. Role-Based Access & Data Security Controls
CRM Software must not compromise on security within Financial Institutions. Several departments receive customer data, and not everyone should have access to all of it.
Security features include:
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Multi-level authentication
- Data encryption
- Audit trails and logs of activities.
- Field-level controls (ex, do not show PAN or SSN to the junior staff)
This guarantees that there is adherence to the laws of data protection of financial information and unauthorized access.
9. Customer Self-Service Portal
The current consumers are digital-first. A self-service portal using CRM leads to less workload in branches and greater satisfaction. Portal capabilities:
- Check loan and account information.
- Upload KYC documents
- Track application status
- Submit service requests
- Schedule an appointment with the relationship managers.
Self-service experiences facilitate greater transparency and lower operational costs.
10. Performance Analytics Dashboard
The management teams must be able to have real-time access to performance at branch, team and product levels. This intelligence is available in real time on a CRM dashboard.
Dashboards may include:
- Loan pipeline analytics
- Branch-wise performance
- Conversion and churn reports.
- Customer satisfaction indicators.
- Compliance and risk measures.
This provides leadership with information-based decision-making and strategic planning.
How Can CRM in Banking Software Improve Customer Retention and Loyalty?

CRM is best for retention. Financial institution CRM software is used to track customer behavior, anticipate customer needs, and propose suitable interactions. CRM assists needs retention:
- Renewal alerts
- Personalized offers
- Cross-sell recommendations
- Premier client management.
- Monitoring of complaint resolutions.
To illustrate, CRM can notify managers when a customer is about to renew their loan or when there is a risk of churn due to inactivity. Individualized interaction enhances trust and life time value.
How to Choose the Right CRM in Banking Software Solution?
Choosing an appropriate CRM system is among the critical technology choices that a financial institution can make. A bank’s CRM affects customer onboarding, loan processing, compliance, and the efficiency of operations across teams in different branches.
Among the available dozens of CRM platforms on the market, banks need to consider how these solutions can be scaled over the long term, integrated, and comply with the regulatory requirements. For a broader view of CRM planning across sectors, you can also study our guide on how to develop your own custom CRM software from scratch.
The following are the main assessment criteria that every bank should adopt when selecting a Banking Software CRM solution.
1. Evaluate Integration Capability With Core Banking Systems
A banking CRM should be integrated with:
- Core banking systems
- Loan origination systems
- Payment gateways
- KYC and AML engines
- Digital onboarding systems
- Call center platforms
Customers lose data due to data fragmentation without real-time information synchronization. Search APIs, middleware compatibility, and established integration experience.
2. Assess Scalability for Branch and Customer Growth
Banks get larger and larger, new branches, new products, new customers. The CRM must:
Extend to thousands of transactions per day.
- Support multiple branch operations.
- Deals with high customer volumes.
- Add modules with no system downtime.
Select a CRM that expands with your institution rather than restricting it.
3. Verify Security, Compliance, and Audit Readiness
CRM Software for Financial Institutions deals with sensitive data; therefore, the solution should contain:
- Encryption of data (at rest and in transit).
- Multi-factor authentication
- Role-based access control
- Automated audit logs
- Ready KYC and AML modules that are compliance-ready.
This ensures regulatory compliance and prevents unauthorised access.
4. Check Workflow Customization Capabilities
Banks have different banking processes. The CRM ought to enable custom workflows of:
- Loan processing
- Credit evaluation
- Customer onboarding
- Document verification
- Cross-sell and upsell campaign.
- Automated reminders
A strict CRM will develop bottlenecks in operations. A adaptable one will conform within your bank, not vice versa.
5. Review Analytics and Reporting Strength
Banking depends on reporting to make decisions. A strong CRM must provide:
- Real-time dashboards
- Performance analytics
- Loan pipeline insights
- Report of customer segmentation.
- Risk and compliance indicators.
This assists the leadership to make informed and data-driven decisions.
6. Consider User Experience and Training Requirements
CRM implementation is unsuccessful when employees are confused by the interface or perceive it as slow. Evaluate:
- Ease of use
- Navigation structure
- Mobile accessibility
- Training requirements
- Multilingual support availability.
CRM must not make work harder, but should make it more productive.
7. Determine Vendor Expertise in Banking and Finance
Banking institutions cannot trust generic CRM. The provider should be aware of:
- Lending workflows
- Compliance rules
- Financial risk models
- Banks Customer Lifecycle.
- Multi-branch operations
A vendor that has a history of working in banking software will minimize implementation risks and speed up ROI.
Conclusion
CRM Banking Software has become the backbone of contemporary financial institutions, integrating customer experiences, regulatory frameworks, and analytics into a single platform. The 10 features mentioned above can assist banks in streamlining workflows, better retention, increasing lending processes, and providing personalized digital experiences at scale.
Bank CRM modules integrated improve operational efficiency, minimise errors, and provide teams with real-time intelligence.
To modernize your banking processes, collaborate with Shiv Technolabs, the best banking software development company, to add CRM features tailored to financial institutions.
At Shiv Technolabs, we offer high-performance Banking software development services, loan automation systems, KYC/AML integrations, analytics dashboards, and data-secure systems designed to be the future of digital banking. Contact us today and make your banking platform a customer-focused digital powerhouse.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the purpose of CRM in Banking Software?
Banking Software CRM assists banks in centralizing customer data, streamlining communication, managing loan journeys, monitoring compliance, and delivering personalized customer experiences. It becomes the online hub for customer interaction.
2. How much does it cost to implement CRM in Banking Software?
The price depends on personalization, integrations, and user base. Implementation ranges from $15,000 to $70,000, depending on complexity, workflows, security options, and data migration requirements.
3. What are the most important CRM features for banks?
The primary characteristics are a 360-degree customer perspective, automated lead-to-loan processes, AI insights, KYC/AML compliance, cross-channel communications, automated tasks, and analytics dashboards.
4. How long does CRM integration take for a financial institution?
The integration process lasts typically 2-4 months in mid-sized banks. Data migration and security alignment may take longer in large banks with custom legacy systems.
5. Is CRM Software for Financial Institutions secure?
Yes, CRM systems are highly secure, meeting financial security standards and regulatory requirements when they are designed to be encrypted, use multi-factor authentication, implement access controls, and maintain audit logs.






















