Table of Contents
Laravel Horizon is a modern queue management dashboard for Laravel that gives teams clear control over background jobs. Companies running laravel development solutions track queues, workers, and failures in one place and respond faster during spikes. If you wonder what Laravel Horizon is, think of it as a visual command center for Redis-backed queues that keeps delivery predictable.
Setup is quick, and the dashboard feels familiar from the first login. You view job throughput, retry counts, and bottlenecks without digging through logs. The tool suits fast-moving products and enterprise apps that depend on steady task processing. In this guide, you’ll learn how Laravel Horizon works, which features matter most, a practical setup flow, and the real benefits for day-to-day work.
What is Laravel Horizon and Why Does It Matter?
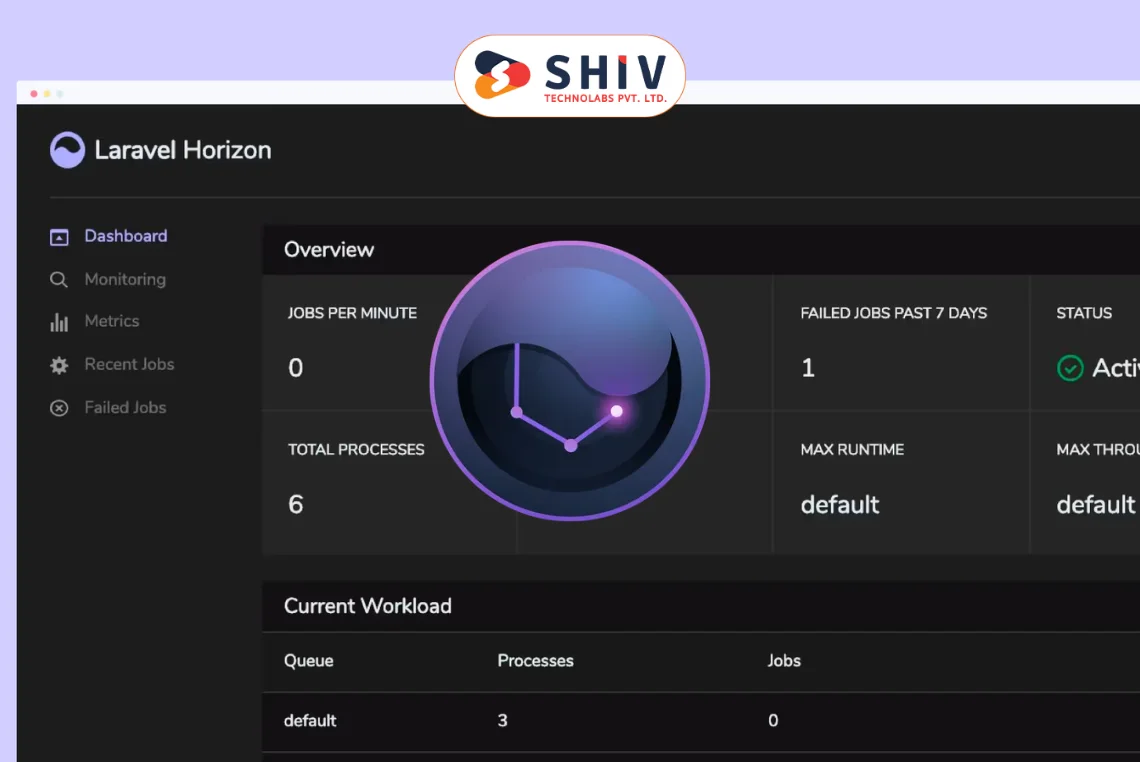
What is Laravel Horizon? It’s Laravel’s queue management layer that turns Redis activity into clear, real-time insights. When teams search “horizon laravel,” they usually want immediate answers on job health, worker capacity, and failure trends. Horizon gives that clarity with live metrics, job history, and simple controls for retries and timeouts.
You manage worker supervision with confidence. Define process counts per queue, assign balance strategies, and keep timeouts aligned with real workloads. Modern Laravel apps offload email, webhooks, media processing, imports, and notifications to queues. Horizon keeps those flows steady, scales with peak demand, and helps you find issues before customers feel the impact.
Comparison Table — Laravel Horizon vs Default Queue Worker
| Feature | Horizon | Default Worker |
|---|---|---|
| Dashboard | Full web UI | No UI, CLI only |
| Retry Count | Configurable per queue/job | Basic |
| Metrics | Throughput, runtime, history | Minimal |
| Alerts | Failure and threshold alerts | None |
| Scalability | Supervisors and balancing | Manual tuning |
How Laravel Horizon Works Behind the Scenes
Horizon sits between your Laravel app and Redis, tracking jobs as they move from queued to processed. It records payload details and job timings, then presents live views of queues and workers. You pick balance strategies, set retry rules, and adjust worker counts to match the current load.
Main Components:
- Supervisors – manage worker processes for one or more queues.
- Workers – run queued jobs pulled from Redis.
- Dashboard – shows live status, failures, and throughput.
- Metrics Storage – captures history for reports and analysis.
Consider a flash sale or a large import where order and invoice jobs spike within minutes. You raise workers for the busiest queues, keep timeouts realistic, and watch trends in real time. If a specific job class fails often, you pause that queue, ship a fix, and restart Horizon to apply the change cleanly. Teams gain faster recovery, clearer visibility, and steadier delivery without guesswork.
How Laravel Horizon Works Behind the Scenes

Horizon connects your Laravel app to Redis and tracks every job from queue push to finish. It records timings, payload data, and outcomes, then shows real-time views for each queue and worker. You adjust worker counts, pick a balance strategy, and set retry rules to match traffic patterns.
Horizon supports three balance strategies: simple, auto, and false for fixed assignments. The auto mode spreads work based on queue load and helps during traffic spikes. Teams also set sensible timeouts per queue, so slow jobs do not block fast ones.
Tags play a key part in Laravel Horizon reporting across large codebases. You tag jobs by feature, tenant, or account to group metrics and speed up debugging. Horizon persists metrics for history, so product and support teams can review past incidents with context.
Supervisors define process pools and restart policies for reliable job handling. During releases, you restart Horizon to pick new code and keep workers consistent. This setup gives predictable results without manual shell checks or ad-hoc scripts.
Key Laravel Horizon Features You Should Know
The following Laravel Horizon features help teams keep queues healthy and developers productive. Many shops searching for “horizon laravel” start here to plan dashboards, alerts, and scaling rules.
Real-Time Dashboard
Get a live view of queues, workers, throughput, and recent failures in one place. Filter by queue, tag, or job class to spot problems quickly and act with confidence.
- Watch queue depth change second by second during traffic spikes.
- Drill into job details to see payloads, runtime, and exception traces.
Queue and Job Metrics
Horizon tracks throughput, runtime distribution, and job counts for each queue. Historical metrics help teams compare weekdays, campaigns, and release windows.
- Review rate charts to plan worker counts for busy periods.
- Share findings with product teams to align expectations during launches.
Job Retries and Failures
Handle failing jobs without guesswork or risky scripts. You can retry jobs from the dashboard and set retry limits per queue or job type.
- Apply different retry rules for mailers, webhooks, or imports.
- Pause a noisy queue, fix the code, then resume processing safely.
Tag Monitoring and Alerts
Use tags to group jobs by feature or client and raise alerts when failure rates rise. Your team learns about problems before users report them publicly.
- Send notifications to chat or email when thresholds trigger.
- Focus on the right queue instead of scanning logs for patterns.
Feature Comparison: Horizon vs Manual Monitoring
| Feature | Laravel Horizon | Manual Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time monitoring | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Alert notifications | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Retry control | ✅ Yes | ⚠️ Partial |
| Dashboard UI | ✅ Modern | ❌ CLI only |
| Historical metrics | ✅ Built-in | ⚠️ Limited |
| Tag-based insights | ✅ Supported | ❌ Not native |
If your team wants fast wins with queues, Horizon offers a clear path. You get rich metrics, live controls, and safer recovery during peak demand. With the right tags, rules, and supervisors, your background jobs stay steady while features ship on time.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Set Up and Use Laravel Horizon
Laravel Horizon installs quickly and gives you clear control over Redis-backed queues. Many developers search for “horizon laravel” while setting up, so this walkthrough keeps steps practical and direct.
Step 1 — Install Horizon
Run the package install command and publish assets for configuration and views. Older projects may add the service provider manually, while newer ones register it automatically.
composer require laravel/horizon php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Laravel\Horizon\HorizonServiceProvider"
Step 2 — Configure Supervisors and Queues
Open config/horizon.php and define supervisors for your busiest queues. Pick a balance mode (simple, auto, or false), then set timeouts, memory limits, and retry counts per queue.
- Use auto to spread workers as load shifts during promotions or imports.
- Keep long jobs on a separate queue, so short tasks keep moving.
Step 3 — Access the Dashboard
Start Horizon and open the dashboard to watch jobs in real time. Use filters by queue, tag, or job class to understand how Laravel Horizon works during normal traffic and peak hours.
php artisan horizon # Visit: https://your-app.test/horizon
Step 4 — Secure the Horizon Dashboard
Limit access to admins using the Horizon authorization callback or a route middleware. Add your rule in Horizon::auth within App\Providers\HorizonServiceProvider.
use Laravel\Horizon\Horizon;
public function boot(): void
{
Horizon::auth(function ($request) {
return $request->user() && $request->user()->isAdmin();
});
}
Step 5 — Monitor and Scale Workers
Watch queue depth, runtime, and failures, then adjust worker counts with confidence. Schedule periodic horizon:terminate so workers reload fresh code after deployments without manual restarts.
// app/Console/Kernel.php
$schedule->command('horizon:terminate')->hourly();
- During a sale or data import, raise workers for the busiest queues and switch to auto.
- After a fix, restart Horizon so workers pick the latest code and configuration.
Common Setup Mistakes to Avoid
- Missing Redis configuration before starting Horizon.
- Leaving the dashboard public without authentication.
- Skipping job tags, which reduces reporting quality and alert accuracy.
- Mixing slow and fast jobs on one queue, causing hidden backlogs.
- Forgetting to restart Horizon after code changes.
- Relying on default retry counts for critical flows.
Why Use Laravel Horizon in Your Projects?

Why use Laravel Horizon? It delivers real-time visibility, quicker recovery, and smoother daily operations for Redis queues. Teams act faster because the dashboard highlights throughput, runtime, failures, and tags with actionable clarity.
Horizon also shortens feedback loops during releases and traffic spikes. Developers adjust worker counts, test retry rules, and pause noisy queues without risky shell scripts or guesswork.
Quick wins you can expect:
- Simplifies queue management for busy Laravel applications.
- Raises reliability with clear alerts and safe retries.
- Saves developer time by cutting manual checks.
- Scale background jobs calmly during peak periods.
Best Practices for Working With Laravel Horizon
Keep Horizon and Redis on current stable versions to avoid hidden bugs and security gaps. Schedule regular reviews of queue depth, runtime trends, and failure spikes so teams act before customer impact.
Tag every important job with clear labels like order, billing, or webhook. Tags help filter charts, trigger alerts, and explain incidents during post-release checks without guesswork.
Separate slow, CPU-heavy jobs from fast, user-facing tasks on different queues. This small change keeps quick actions responsive while larger jobs finish without blocking critical flows.
Protect the dashboard with strict access rules and activity logs. Limit entry to admins and rotate credentials on a set cadence to reduce risk from shared accounts.
Right-size worker counts by day and hour, not just by averages. Plan extra capacity for campaigns, imports, or seasonal surges, then scale back after traffic returns to normal.
Treat retry rules as product decisions rather than defaults. Give mailers and webhooks a few careful attempts, but surface data-import failures quickly to avoid compounding errors.
Conclusion: Manage Queues With Laravel Horizon
Laravel Horizon brings clear control to background processing, real-time visibility to worker health, and faster recovery during spikes. Teams build steadier features because they can watch throughput, spot failures, and adjust workers in minutes.
If you’re planning to integrate advanced queue systems or need expert Laravel support, reach out to a trusted laravel development company to build reliable and scalable applications.
FAQs About Laravel Horizon
Q1: What is Laravel Horizon used for?
Laravel Horizon gives a real-time dashboard for Laravel queues, showing throughput, runtime, failures, and job history. Teams use it to track workers, tune retries, and act quickly during incidents.
Q2: How does Laravel Horizon work with Redis?
Horizon connects to Redis for queue storage, then records timing and status details for every job. It displays live metrics, which makes analysis and troubleshooting faster.
Q3: Can I run Laravel Horizon without Redis?
No, Horizon is built for Redis-backed queues and depends on that connection. If you need other drivers, use the default queue worker or switch the project to Redis first.
Q4: What are the main Horizon features?
You get a real-time dashboard, tag-based filtering, job retries, and alert notifications. Historical metrics also help teams review incidents and plan capacity with confidence.
Q5: Is Laravel Horizon good for large-scale apps?
Yes, it suits multi-queue and multi-supervisor setups where traffic changes quickly. Teams can add workers, adjust balance modes, and keep user-facing actions responsive during busy periods.
Q6: How should I secure the Horizon dashboard?
Limit access through the Horizon::auth callback and strict admin roles. Review logs often, rotate credentials, and avoid shared passwords to reduce risk.