Table of Contents
Generative AI applications are changing how digital products work. Instead of following fixed rules or predefined flows, these apps create text, images, code, or responses based on user input and context. Businesses are using GenAI apps to handle repetitive tasks, speed up content creation, support customers, and assist internal teams.
GenAI app development focuses on building software that connects AI models with real business workflows. These apps can answer questions, draft content, summarize data, or assist users in real time. The goal is not automation alone, but smarter interaction that feels natural and useful.
This guide explains GenAI app development in a practical way. It covers real use cases, key features, cost factors, and the steps involved in building a GenAI application. Whether you are planning a new product or adding AI capabilities to an existing system, this content will help you understand what goes into building a reliable GenAI app.
What Is GenAI App Development?
GenAI app development is the process of creating applications that can generate new output instead of only showing stored data. These apps use generative models to produce text, images, audio, code, or structured responses based on user input and past context.
Unlike traditional software, GenAI apps do not rely on fixed logic paths. They analyze prompts, understand intent, and respond with fresh output each time. This makes them useful for tasks where responses cannot be fully predicted in advance.
A typical GenAI application includes:
- A user interface where users enter prompts or requests
- An AI model that processes input and creates output
- Backend services that manage data, rules, and access control
- Logging and monitoring systems to track usage and quality
GenAI app development is not limited to chat systems. It also includes tools for content creation, internal automation, decision support, and developer assistance. The focus is on building reliable systems where AI output supports real business goals while staying controlled and secure.
How GenAI Applications Work

GenAI applications follow a structured flow behind the scenes, even though the user experience feels simple. Each request passes through multiple layers before the final output is shown.
First, the app captures user input. This can be text, voice, images, or a combination of inputs. The system cleans and formats this input so the AI model can understand it clearly.
Next, the app applies prompts and context rules. Prompts guide the model on how to respond, what tone to follow, and what limits apply. Context may include past messages, user role, or business data pulled from databases.
The AI model then processes the request. Based on its training and the provided prompt, it generates a response in real time. This output is not stored text; it is created during the request.
After generation, the system applies filters and checks. These steps help remove unwanted content, control length, and match business rules. In some cases, outputs are reviewed by humans or adjusted using feedback logic.
Finally, the response is delivered to the user through the app interface. Usage data, errors, and feedback are logged so the system can be improved over time.
This layered approach allows GenAI apps to stay flexible while remaining controlled and reliable for business use.
Popular GenAI App Use Cases Across Industries
GenAI applications are being adopted across multiple sectors because they can handle tasks that require language understanding, pattern recognition, and content creation. Below are some of the most common use cases seen in real business environments.
1. GenAI in Customer Support
GenAI apps are widely used to manage customer conversations. These systems can answer common questions, explain products, and guide users through processes without fixed scripts.
Common use cases include:
- AI chat systems for websites and apps
- Drafting replies for support agents
- Summarizing long support tickets
- Handling after-hours customer queries
2. GenAI in Marketing and Content Teams
Marketing teams use GenAI apps to reduce time spent on writing and editing tasks. These tools help generate first drafts that teams can review and adjust.
Typical uses include:
- Blog and article drafting
- Ad copy suggestions
- Email campaign content
- Social media post ideas
3. GenAI in Software Development
Developers use GenAI tools to speed up routine coding tasks and reduce manual debugging effort.
Use cases include:
- Code suggestions and explanations
- Test case writing
- Error message breakdowns
- API documentation drafts
4. GenAI in Healthcare
Healthcare-focused GenAI apps assist medical professionals with documentation and patient communication, while keeping humans in control of final decisions.
Common examples include:
- Medical note drafting
- Patient query assistants
- Clinical summary generation
5. GenAI in Finance
In finance, GenAI apps help teams work with large volumes of text-based data and reports.
Use cases include:
- Financial report summaries
- Policy and document analysis
- Risk assessment notes
6. GenAI in E-learning and Training
Education platforms use GenAI apps to create adaptive learning experiences for students and professionals.
Examples include:
- AI tutors
- Study material generation
- Quiz and assessment creation
These use cases show how GenAI apps fit into daily workflows across industries, supporting teams without replacing human judgment.
Core Features of a GenAI Application
A GenAI application needs more than an AI model to work well in real business scenarios. The right features help control output, protect data, and support consistent user experiences.
1. Natural Language Input Handling
GenAI apps must understand user queries written in plain language. This includes handling incomplete sentences, follow-up questions, and different writing styles.
2. Context Memory and Session History
The app should remember past interactions within a session. This helps the AI give relevant responses without users repeating information.
3. Multi-language Support
Many businesses require GenAI apps that can read and respond in more than one language, based on user preference or region.
4. Role-based Access Control
Different users may need different permissions. Admins, staff, and end users should see and access only what applies to them.
5. Output Control and Safety Filters
These controls help limit response length, remove unwanted content, and follow business rules. They are critical for public-facing applications.
6. Human Review and Feedback Loop
Some GenAI apps allow humans to review AI responses before final use. Feedback is also used to improve prompt quality and results.
7. Analytics and Usage Tracking
Tracking how users interact with the app helps teams understand performance, costs, and areas that need improvement.
Together, these features help GenAI applications stay reliable, secure, and useful for daily operations.
Types of GenAI Apps Businesses Build
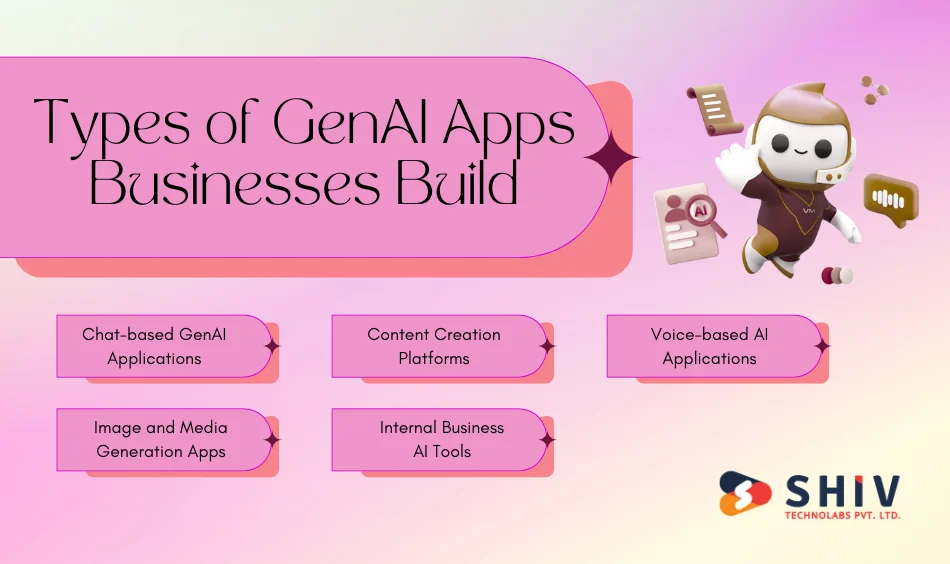
GenAI technology can be shaped into different types of applications depending on business goals and user needs. Below are common GenAI app formats seen across industries.
1. Chat-based GenAI Applications
These apps allow users to interact through text or voice. They are often used for customer support, internal help desks, and virtual assistants.
2. Content Creation Platforms
These tools focus on generating written or visual content. Businesses use them for blogs, product descriptions, marketing copy, and design ideas.
3. Voice-based AI Applications
Voice-driven GenAI apps accept spoken input and return spoken responses. They are used in call centers, mobile apps, and smart devices.
4. Image and Media Generation Apps
These applications create images, graphics, or videos based on text prompts. They are popular in design, media, and advertising workflows.
5. Internal Business AI Tools
Some GenAI apps are built only for internal use. These tools help teams draft reports, summarize meetings, or search internal knowledge bases.
Each type serves a different purpose, but all rely on controlled AI output and strong backend systems to support real-world use.
GenAI App Tech Stack Overview
A GenAI application relies on multiple technical layers working together. Each layer has a clear responsibility, from handling user requests to managing AI responses and data security. The table below breaks down the typical tech stack used in GenAI app development.
| Tech Stack Layer | Purpose | Common Tools & Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Frontend | Manages user interaction, input capture, and response display | React, Next.js, Vue, Flutter |
| Backend | Handles business logic, API routing, and user roles | Node.js, Python, Java, .NET |
| AI Models | Generates text, images, or other outputs based on input | GPT-based models, Claude, open-source LLMs |
| AI Integration Layer | Connects the app with AI models and manages requests | REST APIs, SDKs, model gateways |
| Vector Database | Stores embeddings for search and context matching | Pinecone, Weaviate, FAISS |
| Data Storage | Stores user data, logs, and app configurations | PostgreSQL, MongoDB, MySQL |
| Security Layer | Controls authentication and data access | OAuth, JWT, role-based access |
| Monitoring & Logs | Tracks usage, errors, and performance | Prometheus, Grafana, ELK stack |
This tech stack can vary based on app size and industry needs. Some applications require stronger security layers, while others focus more on response speed and model performance.
Choosing the right combination of tools helps keep the GenAI application stable, controlled, and ready for long-term use.
Step-by-Step GenAI App Development Process
Building a GenAI application needs more than connecting an AI API and shipping a UI. To get stable output, controlled costs, and a product that fits real workflows, the build process should follow clear stages.
Step 1: Business Requirement Analysis
This stage defines what success looks like and what the app must not do.
What teams usually finalize here:
- Primary goal: support, content, internal assistant, sales enablement, knowledge search, or automation
- Users: customers, internal teams, admins, partners
- Output types: short answers, long-form drafts, structured JSON, summaries, or multi-step guidance
- Accuracy expectations and risk level (public-facing vs internal-only)
- Data needs: what the AI can access (policies, product docs, CRM data, orders, tickets)
- Compliance needs: PII handling, audit logs, retention rules, access boundaries
Deliverables:
- Use case list with priority (must-have vs later)
- User flow map and success metrics (response quality, time saved, resolution rate)
Step 2: Use Case and Model Selection
Model choice affects quality, latency, and cost. This stage decides whether to use a hosted model API, a private deployment, or a hybrid setup.
Key decisions:
- Model type: text-only LLM, image model, voice model, or multi-modal
- Hosting: API-based vs self-hosted (based on security and cost)
- Context size requirements: short context vs long documents
- Language requirements and domain fit (support tone, technical writing, legal style)
- Cost planning: expected monthly volume and peak loads
Deliverables:
- Selected model(s) and fallback plan
- Cost estimate per 1,000 requests (or per user)
- Quality benchmarks for acceptance testing
Step 3: Data Preparation and Prompt Design
This stage controls how the model behaves. It also prepares internal data if the app needs company knowledge.
Work included:
- Prompt templates for different tasks (answer, draft, summarize, classify, extract)
- Guardrails in prompts: tone rules, safe output limits, “ask questions when unclear” logic
- Knowledge setup (if needed): document cleanup, chunking, metadata tagging
- Retrieval layer design (RAG): how the app fetches the right context before generation
- Evaluation set creation: 50–200 real test queries and expected outcomes
Deliverables:
- Prompt library + versioning rules
- Knowledge base structure (docs, categories, update process)
- Test dataset for quality scoring
Step 4: Backend and API Development
The backend is where control happens. It decides what context goes to the model and what rules apply.
Backend usually includes:
- Authentication and role-based access
- Request routing (which prompt + which model for a given action)
- Data connectors (CRM/ERP/ticket system/product database)
- Rate limits, retries, and timeouts
- Caching for repeated questions (to reduce cost)
- Logging: prompts, outputs, user feedback, and system errors
Deliverables:
- API endpoints for the UI and integrations
- Security rules and audit logs
- Cost-control logic (limits, caching, quotas)
Step 5: Model Integration and Testing
This stage validates output quality and catches failure patterns before users do.
Testing typically covers:
- Accuracy checks across common and edge queries
- Hallucination handling: “I don’t know” behavior and source-based answers
- Output formatting: bullet points, JSON, tables, or strict templates
- Safety checks: blocked topics, profanity, sensitive content handling
- Load testing: latency under peak traffic
- Regression testing when prompts or model versions change
Deliverables:
- Quality report (pass/fail by scenario)
- Final prompt tuning updates
- Release checklist for production readiness
Step 6: UI Development
The UI should make GenAI easy to use and hard to misuse.
UI elements often included:
- Clear input hints (examples, required fields, tone selection)
- Response actions: copy, regenerate, shorten, expand, cite sources, export
- Feedback buttons: helpful/not helpful + reason selection
- Conversation memory controls: reset, save, share, private mode
- Admin panel (optional): prompt edits, knowledge updates, user limits
Deliverables:
- Web or mobile UI ready for real usage
- Admin interface for monitoring and controls
Step 7: Quality Checks and Launch Readiness
Before launch, teams confirm stability, security, and predictable operating costs.
Final checks include:
- Security review (PII masking, access controls, encrypted storage)
- Monitoring setup: latency, error rate, cost spikes, token usage, downtime
- Production rollout plan: staged release, rollback, model fallback
- Post-launch support plan: bug fixes, prompt updates, knowledge refresh schedule
Deliverables:
- Production release + monitoring dashboards
- Support and maintenance plan
- Roadmap for phase-2 improvements
Cost of GenAI App Development

The cost of building a GenAI application depends on how complex the use case is and how much control is required over data, output quality, and scale. Unlike traditional apps, GenAI systems also include ongoing model usage costs, which need to be planned from the start.
1. Key Factors That Affect GenAI App Cost
Several elements influence the final development and operating cost:
- Use case complexity: Simple chat or content tools cost less than multi-role, data-connected systems.
- Model type and usage volume: Larger models and high request volumes increase monthly API or hosting costs.
- Custom data integration: Apps connected to internal documents, CRMs, ERPs, or support systems need more development effort.
- Security and compliance needs: Applications handling sensitive data require additional controls, audits, and testing.
- User scale and traffic: Public-facing apps need stronger infrastructure and monitoring than internal tools.
2. Estimated GenAI App Development Cost Ranges
Below are general cost ranges based on typical project scopes. Actual pricing may vary based on requirements.
| App Type | Scope | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|
| MVP GenAI App | Basic chat or content tool, limited users | $15,000 – $30,000 |
| Mid-Scale Business App | Data-connected, role-based access | $30,000 – $70,000 |
| Enterprise GenAI System | High traffic, strict controls, custom workflows | $70,000 – $150,000+ |
3. Ongoing Costs to Plan For
GenAI apps have recurring expenses that continue after launch:
- AI model usage (per request or token-based pricing)
- Cloud hosting and storage
- Monitoring and logging tools
- Prompt updates and quality tuning
- Support and maintenance
For many businesses, ongoing costs are managed by setting usage limits, caching responses, and refining prompts to reduce unnecessary requests.
Planning both development and operational costs early helps avoid unexpected spending as the app grows.
Common Challenges in GenAI App Development
While GenAI applications offer strong value, they also come with challenges that teams must address early. Ignoring these issues can lead to unstable output, rising costs, or user trust problems.
1. Output Accuracy and Consistency
GenAI models can sometimes produce incorrect or misleading responses. This is a concern for apps that share factual, legal, or technical information. Clear prompts, controlled context, and validation layers help reduce this risk.
2. Handling Sensitive Data
Many GenAI apps work with internal documents or user data. Without proper access control and masking, there is a risk of exposing private information. Security planning must be part of the core architecture.
3. Cost Management
Model usage costs grow with traffic. Without limits, caching, or request controls, expenses can increase quickly. Monitoring usage patterns is critical for long-term stability.
4. Context Management Issues
If too much or too little context is passed to the model, responses may lose relevance. Designing proper context rules takes testing and refinement.
5. Scaling for Real Users
Apps that work well in testing may struggle under high load. Response delays and timeouts can impact user experience if scaling is not planned.
6. User Trust and Adoption
If users do not understand how to interact with the AI or see inconsistent results, adoption slows. Clear UI guidance and feedback options help build confidence.
Addressing these challenges early helps teams build GenAI apps that users trust and rely on daily.
Best Practices for Building Reliable GenAI Apps
Reliable GenAI applications are built with control, testing, and feedback at every stage. Following proven practices helps teams avoid common mistakes and maintain quality as usage grows.
1. Write Clear and Focused Prompts
Prompts should define the task, tone, and expected output format. Avoid vague instructions. Break complex tasks into smaller steps when needed.
2. Limit What the Model Can Access
Only pass the data required for each request. This reduces incorrect responses and protects sensitive information.
3. Validate and Structure Outputs
For critical workflows, require structured output such as lists, tables, or JSON. Add checks to confirm responses match the expected format.
4. Add Feedback Loops
Allow users to mark responses as helpful or not. This feedback helps refine prompts and improve response quality over time.
5. Monitor Usage and Costs
Track request volume, response time, and token usage. Early alerts help control spending and performance issues.
6. Plan for Model Updates
Models change over time. Test new versions before switching and keep fallback options ready.
7. Keep Humans in Control
For high-risk tasks, include human review before final use. GenAI should support decisions, not replace responsibility.
These practices help GenAI apps stay stable, cost-aware, and useful in real business environments.
Why Choose Shiv Technolabs for GenAI App Development?
GenAI applications need careful planning, controlled output, and strong backend systems. Shiv Technolabs builds GenAI apps that align with real business workflows instead of surface-level AI features.
The focus stays on clarity, stability, and long-term usability. Each GenAI solution is planned around how teams actually work, what data can be accessed, and how responses should behave in real scenarios.
Shiv Technolabs supports businesses at every stage of GenAI app development, from early planning to post-launch improvements.
Key strengths include:
- Clear use-case definition based on business goals
- Custom prompt design and response control
- Secure data handling with role-based access
- Scalable backend architecture for growing usage
- Cost-aware model usage planning and monitoring
- Ongoing support for updates, testing, and refinements
This approach helps businesses launch GenAI applications that are reliable, controlled, and suitable for daily operations. So why wait? Contact Shiv Technolabs today and start with the development.
Moving Forward
GenAI app development is reshaping how software handles communication, content, and decision support. These applications create real value when they are built around clear use cases and real workflows rather than experimental features.
Successful GenAI apps depend on controlled output, secure data access, and cost-aware design. From model selection to post-launch monitoring, every step affects reliability and user trust.
Businesses that invest time in planning, testing, and long-term support are more likely to build GenAI applications that remain useful as usage grows. With the right development approach, GenAI apps can become a dependable part of everyday operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a GenAI application?
A GenAI application is software that creates new output, such as text, images, or summaries, based on user input. It does not rely only on stored data or fixed rules.
2. How is a GenAI app different from traditional AI software?
Traditional AI follows predefined logic and rules. GenAI apps generate fresh responses each time, based on context, prompts, and trained models.
3. Which industries benefit most from GenAI apps?
Customer support, marketing, healthcare, finance, education, and software teams benefit the most, especially where language and content play a key role.
4. What type of data is required to build a GenAI app?
Some apps work with public data only. Others connect to internal documents, product details, support tickets, or databases, depending on the use case.
5. Are GenAI applications safe for business use?
Yes, when built with access control, data masking, logging, and output filters. Security planning is a core part of GenAI app development.
6. How long does it take to build a GenAI application?
A basic app can take 4–6 weeks. More advanced, data-connected systems may take 8–16 weeks based on complexity.
7. Can a GenAI app work with existing business systems?
Yes. GenAI apps can connect with CRMs, ERPs, ticketing tools, knowledge bases, and other internal systems through APIs.
8. How is response accuracy controlled in GenAI apps?
Accuracy is managed through prompt rules, limited context access, structured output formats, and feedback-based improvements.
9. What ongoing costs are involved after launch?
Ongoing costs usually include AI model usage, hosting, monitoring tools, and periodic updates to prompts and data sources.
10. Can GenAI apps support multiple languages?
Yes. Many GenAI models support multiple languages and can respond based on user preference or region.
11. Is custom model training required for every GenAI app?
No. Many apps work well with existing models and custom prompts. Custom training is needed only for highly specific domains.
12. What kind of support is needed after the GenAI app goes live?
Post-launch support includes monitoring performance, refining prompts, updating data sources, managing costs, and handling user feedback.























